Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
What is Diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis of the colon is a common condition affecting many Americans who are middle-aged or older. Approximately 50% of people over age 50 have diverticula. Only a small percentage of these people eventually require treatment. Diverticulosis is the presence of pockets (diverticula) that develop on the wall of the large intestine or colon. They occur at weak areas in the bowel wall and are most often found on the left side (called the sigmoid colon), but they can be found anywhere throughout the colon.
What Causes Diverticulosis?
Diverticula occur gradually over time and are due to excessive pressure or spasms within the bowel. The amount of fiber and fluid intake affects what kind of action occurs in the bowel. The American diet is high in processed foods which have had the natural fiber removed. When fiber and fluid are lacking, the stool becomes hard and dry. The muscles in the wall of the colon need to squeeze with greater force, causing a bulge to form in the colon wall, which eventually becomes a pocket or diverticulum. Learn more about a High Fiber Diet.
What are the Symptoms of Diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis presents in several different ways. Most people with diverticulosis have no symptoms. If they do, possible symptoms include left lower abdominal pain, diarrhea, cramps, and change in bowel habits. Some patients with diverticulosis can have severe rectal bleeding. These symptoms can also be the result of other conditions. An examination is necessary to make the correct diagnosis.
What Can I Do to Prevent Diverticulosis?
The prevention of diverticulosis and treatment of its symptoms are managed in the same way – with diet and occasionally with medication You should increase your intake of dietary fiber to 25 grams daily and liquid to 8-10 glasses daily. High-fiber foods and commercial fiber products add bulk to the diet, which helps achieve regular bowel habits. Fiber holds water, which helps to soften the stool. Soft stool requires less pressure to move it through the colon. Diverticula formation may be reduced or even stopped.
What is Diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is an infection in a diverticulum or pocket in the colon. It occurs when the opening of a diverticulum is blocked with stool and the diverticulum ruptures, resulting in a localized infection. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, chills, fever or change in bowel habits.
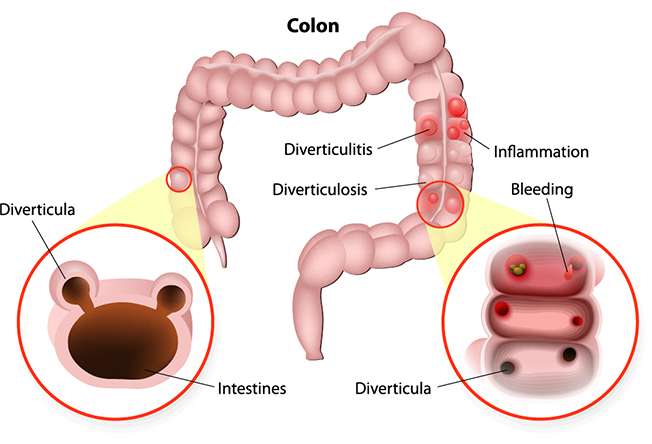
Complications can result in bowel perforation, abscess or infection into another organ. Mild cases can be managed at home with oral antibiotics and a modified diet. Severe cases require hospitalization with intravenous antibiotics and no food or fluid by mouth. Surgery becomes necessary with recurrent episodes, complications, or a poor response to medications.
When surgery is required, the affected part of the colon is removed and the remaining colon reconnected. Bowel activity typically returns in three to five days and becomes routine in approximately three weeks.
To learn more or schedule a second opinion please contact our Concierge Patient Coordinator at (210) 490-2828 or toll free at (866) 259-3778.